How to Recover from a Thin Content Penalty
There’s 12 different manual penalties that can be enforced on a site by Google and many of these are pretty straightforward. For instance, unnatural links coming from the site means a user needs to remove all those spammy links and request to be reconsidered by Google. However, the Thin Content penalty can be a bit confusing and there are a few steps that need to be addressed before the penalty can be removed by you or by the team of qualified experts experienced in removing SEO penalties.
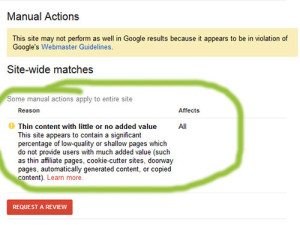
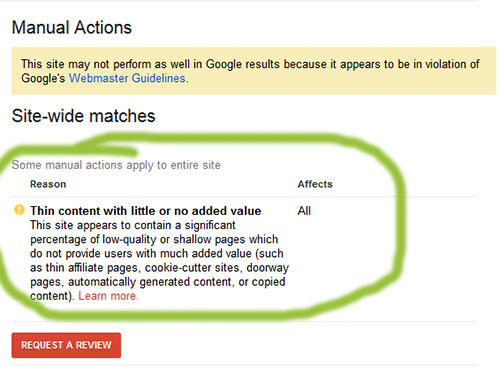
Thin content is defined as content with ‘little or no added value’. Now what does this exactly mean? There’s lots of theories behind content, the saying use to go “content is king”, now this is still relevant, however, it needs to be content that adds value. Many websites will create content just to have content, search engines, and most importantly users, don’t want to see this type of content.
Types of poor quality content.
Occasionally content marketers will attempt to increase their site’s rankings by creating content with lots of keywords and phrases, but no genuine content. These domains will be flagged by Google which result in a penalty, thus affecting the rankings and organic traffic to the site. So what types of content does Google want to be avoided?
Autogenerated content – Auto-generated content is typically content that is created by some type of program. It may be pulled from a RSS feed or even scraped from multiple websites related to a specific keyword. It is unreadable to users, however it’s designed to utilize keywords within the jumble of words which is suppose to increase the site’s rankings. This is a prime example of content that does not add any value. This content is not fluid sentences, not reviewed by an actual person, and does not provide any helpful information to users.
Doorway Pages – These are pages or even sites that may be ranking well in the search results, yet when a user clicks to the page they are taken to another page unrelated to their click. This is misleading to the users and leads to poor user experience which Google has made one of their top priorities. Approaches like this are often done by webmasters who are trying to funnel users to a certain part of a site, rather than where they originally clicked.
Scraped content – Sites that don’t take their time to build their own content will often scrape content from other, more established websites. As mentioned before, Google wants content that adds value, content that is blatantly plagiarized from other sources is not adding any value. This content can be scraped and slightly altered, often done by some type of program. A majority of the time certain words or synonyms will be changed out to make the content appear as their own. Search engines have the ability to determine if this type of content is copied from other sources.
Thin affiliate sites – Google looks at affiliate sites as a violation of their guidelines, simply because affiliate sites are often using another site’s information, products, content, etc. However, there are ways to have a successful affiliate site that won’t be penalized by Google. To accomplish this it is recommended that affiliate sites create their own content, navigation, product categories, and product listings. This will show the search engines the site is unique and provides its own value to users.
Determining if your site has been penalized.
The first sign of a thin content penalty is a drop in organic traffic or rankings. Once a webmaster sees this their next action is to review Google’s Search Console to see if there’s been any unusual activity. Within the Search Console dashboard, under the Search Traffic drop down, users can find a list of manual actions against their site. The penalty will mention a thin content penalty, however won’t go into much detail on where it is or how to find it.
Webmasters will need to determine where this content exists to locate and fix or remove. Depending on the size of the website this can be very time consuming, yet necessary. Webmasters need to review their site along with their content plan to locate what pages or page the penalty affected.
There are some steps to locating penalized pages and these include the following. Read your content out loud, does it make sense? Are the sentences complete thoughts? If the content is a bunch of mumbled together sentences this can be the root of the penalty. Next think of any pages that may have been copied. This can include product reviews, category pages, or even frequently asked questions. Finally, are there any misleading pages? Pages that may appear to take a user one place, but redirects them to a completely different page.
How to remove and fix a thin content penalty
Once the penalized pages have been identified it will be time to fix and/or delete these pages. Again this can be a lengthy process if the site has thousands of pages that are being penalized. However, each one of these pages needs to be fixed before the penalty can be lifted. There’s two simple steps to the content dilemma.
- Delete it – The straightforward, fastest approach is to simply delete all the content that has been copied or autogenerated from other sources. Now many webmasters are hesitant of this approach because the site is at risk of losing a number of pages. If these pages are deleted it’s best to replace this content with your own, new content. Again, very time consuming.
- Rewrite it – Option number two is to rewrite all the pages that were affected. This is the best approach for sites that have copied product descriptions from a manufacturer’s site. Webmasters will need to revisit all pages that have copied content and rewrite the content to their own ideas. Also a time consuming process, yet all the pages still exist. If any of these pages ranked well before the penalty chances are it can rank well again once the content is updated. Make sure you are not just rewriting content but also increasing engagement with custom content builders that let’s you add interactivity.
Submit a reconsideration request to remove the penalty
Once the content has been fixed it will be time to submit a reconsideration request to Google through Search Console. The reconsideration request is a bit different than a link removal where a disavow list is not needed. This letter will mention the process the webmaster has gone through to remove the penalty. Helpful information to add to this letter includes a screenshot from a plagiarism tool (such as CopyScape) showing the site has no duplicate content issues. Another piece of information to add in the letter is to show which pages were updated. Although this is not necessary it can help show the process that was completed to remove the penalty. Keep in mind that it is rare the first request is often denied forcing sites to review additional pages.
